Automatic Identification and Data Collection (AIDC) is a technological model that automates the process of identifying objects, entities, or transactions and gathering their related data. Organizations can use AIDC technologies like barcodes, biometrics, and voice recognition to streamline the data collection process and eliminate the need for labor-intensive and often unsecure manual data entry. This article explains how AIDC works and how firms across various industries are using it to automate their data identification and collection efforts.
What is Automatic Identification and Data Collection (AIDC)?
Automatic identification and data collection—sometimes also referred to as automatic identification and data capture—is a category of related technologies used to collect data without manual intervention. Data can be collected from an individual person or from an object, image, or sound, among other things. From unlocking your phone to scanning groceries at the self-checkout aisle, chances are you interact with AIDC technologies every day.
Consider some of the most common applications of AIDC technology and how often you encounter them:
- Barcodes and QR codes
- Magnetic stripes (credit cards, hotel key cards)
- RFID chips
- Biometrics (fingerprint scanners, facial recognition)
The use of AIDC technology can enhance efficiency and security and improve the accuracy and reliability of collected information. Many organizations use AIDC in an extensive array of applications, from inventory management to product tracking to secure access and ID control to interactive product marketing.
How Does AIDC Work?
AIDC works by orchestrating a series of technologies—hardware, software, and communication protocols—to create a seamless flow of data identification and collection processes. These processes are carried out in several stages.
Data Encoding and Capture
Many AIDC use cases start with users interacting directly with a device to scan a QR code or undergo a biometric scan—for example, when logging securely into a PC or operating system. This might be for accessing product information or gaining secure access to physical spaces or digital platforms.
In all scenarios, AIDC starts with encoding relevant information into a specific data format for processing. This can take the form of barcodes and biometric identifiers or similar encoding formats such as quick response (QR) codes and radio frequency identification (RFID) chips like those found in toll booth transducers.
The encoded data encapsulates various attributes like user authentication credentials, product details, manufacturing dates, pricing, or geographical location. Specialized devices designed to capture the encoded data from physical objects or entities are then used to read the data.
Data Transmission and Processing
Captured AIDC data is then sent to a designated system or server for real-time data processing over a wired connection such as USB and ethernet, or using wireless technologies like WiFi, Bluetooth, and cellular networks.
Once transmitted, the collected data undergoes various processing activities, typical data validation, analysis, transformation, and integration into overarching enterprise systems like customer relationship management (CRM) systems or business intelligence (BI) platforms. This crucial phase converts raw data from the field into actionable insights for guiding strategic decision-making processes.
What is AIDC Used For?
Due to its general automation benefits and adaptability to specific industries and use cases, AIDC has become a staple in a wide range of applications and industries, from retail and logistics to healthcare and finance. Here are some of the most common enterprise applications for AIDC.
Identification, Access Control, and Security
Biometric AIDC systems ensure secure access to physical spaces, computer networks, and confidential information. One of the earliest and most common AIDC use cases involves using a key card to access an office building.
Manufacturing, Logistics, and Warehousing
AIDC enhances production efficiency by enabling the real-time tracking of raw materials, work-in-progress items, and finished goods, resulting in streamlined operations and reduced downtime. For example, supplier data, material inventory levels, and machine performance can be accessed and tracked throughout the production process using a combination of AIDC technologies—typically IoT and sensor devices. Once items, products, or orders are assembled, AIDC facilitates precise shipment tracking, reducing errors, enhancing order fulfillment, and enabling efficient route optimization.
Medicine and Healthcare
Even the most typical, non life-threatening medical and healthcare scenario calls for minimal errors and an exceedingly high degree of accuracy and precision. To this end, AIDC is being used to quickly onboard new patients—for example, scanning and updating patient status and vitals quickly through different departments—and proactively track patient health and wellness. It’s also used widely in medication management through the use of auto-refilling prescriptions using QR codes and medical equipment monitoring.
Parking and Transportation
AIDC-based systems are employed in toll collection, electronic ticketing, and vehicle identification, enhancing traffic management and reducing congestion. For city dwellers in particular, AIDC is a highly visible, common fixture—from barcode scanning solutions for access control to parking lots to barcode-based ticket validation devices at train stations.
Retail and Inventory Management
AIDC technologies like barcodes and RFID tags have revolutionized inventory tracking, enabling retail and shipping enterprises to implement real-time stock monitoring and more efficient supply chain management.
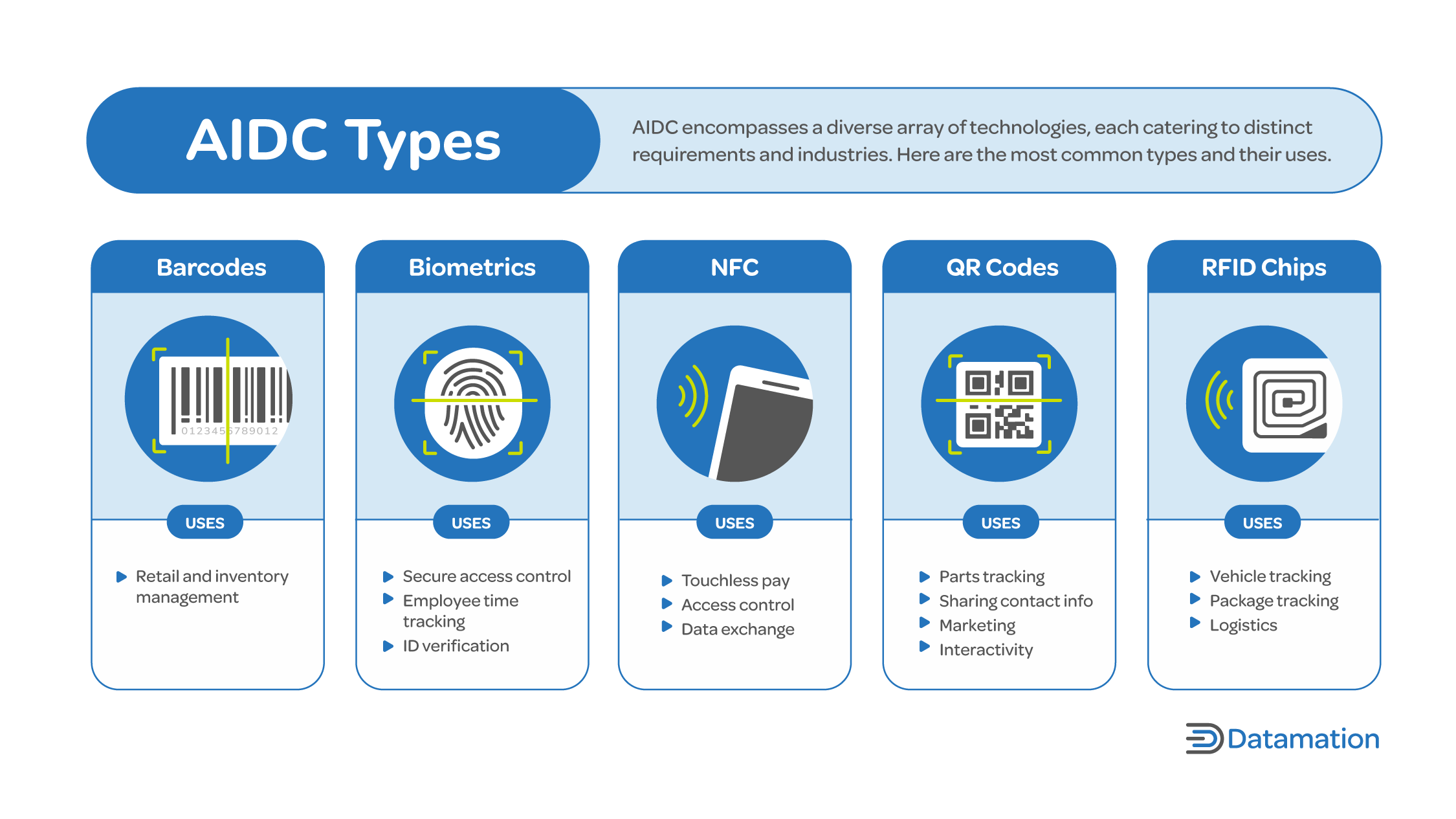
AIDC Types
AIDC encompasses a diverse array of technologies, each catering to distinct requirements and industries. The following is an overview of the most prominent types.
Barcodes
Barcodes are the oldest, most basic of AIDC types, invented over 70 years ago. The technology itself has changed relatively little since then—barcodes consist of patterns of parallel lines of varying widths that together represent data when scanned by a barcode reader. These days, this elemental AIDC type is a cornerstone of retail and inventory management, offering a cost-effective and efficient solution for standardized data collection across industries.
Biometrics
Biometric AIDC uses a person’s unique physiological or behavioral traits for identification purposes. Common biometric identifiers include fingerprints, iris patterns, facial features, voiceprints, and even gait patterns derived through visual analysis. The Biometrics Institute has defined 16 different types of biometrics for automatically identifying people by their unique physical characteristics.
Because they offer a high level of security and accuracy, biometrics are ideal for applications that demand stringent security and strong authentication measures (e.g., secure access control, employee time tracking, and identity verification).
| DNA | Ear shape/features | Eyes—iris | Eyes—retina |
| Eyes—scleral vein | Face | Finger geometry | Fingerprint |
| Gait | Hand geometry | Heartbeat | Keystrokes (typing) |
| Odor | Signature | Vascular (vein) | Voice |
The Biometrics Institute has identified and defined 16 types of biometrics that can be used to automatically identify people by their unique physical characteristics.
Near Field Communication (NFC)
NFC is a subtype of RFID that enables short-range communications between devices. NFC-enabled devices can establish connections by being in close proximity, typically within a few centimeters, for applications in contactless payment systems, access control, and data exchange between devices like smartphones and point-of-sale terminals.
QR Codes
A close cousin of the barcode, the QR code was developed for parts tracking during the automobile assembly process. These two-dimensional barcodes are capable of storing more data than traditional linear barcodes and can support a wide range of data types, including website URLs, contact information, product details, and more. QR codes have gained immense popularity due to their versatility, enabling marketers to engage customers with interactive content and information.
RFID
RFID technology uses radio frequency signals to enable wireless communication between an RFID tag and a reader. RFID tags come in passive and active form. Passive tags derive power from the reader’s signal and are suitable for applications like inventory management and supply chain tracking. Active tags have their own power source and can transmit data over longer distances, making them suitable for scenarios such as vehicle tracking and large-scale logistics.
Benefits of AIDC
Though AIDC technologies have been around for some time, they remain relevant due to their balance of simplicity, efficiency, security, and affordability. Each of the many types of AIDC offers a unique set of advantages—they should be selected based on application requirements, industry standards, and specific security considerations, among other factors. Regardless of the type, firms that implement AIDC technologies generally realize a wide range of benefits. Here are some of the most prominent.
Accuracy and Efficiency
AIDC systems virtually eliminate errors associated with manual data entry, leading to more accurate and reliable data collection. By eliminating typos and human mistakes, organizations can achieve a high level of data accuracy and more reliable strategic decision-making. The automation of data collection reduces the time required to gather information, allowing employees to focus on more high order, value-added tasks. This optimization of human resources in turn boosts the enterprise’s overall operational efficiency.
Enhanced Customer Experience
AIDC technologies are especially prevalent in retail environments where they enhance customer experiences by simplifying processes like product information requests and checking out/completing purchases. By expediting and automating these previously high-touch interactions, AIDC helps to enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty through shorter wait times and smoother interactions.
Real-Time Insights and Inventory Management
AIDC technologies provide real-time data, enabling businesses to make informed decisions promptly. This agility enables organizations to respond promptly to changing conditions in response to market conditions and competitive activity. In retail, logistics, and warehousing, AIDC expedites and streamlines inventory tracking, helping to minimize stock-outs and reduce excess inventory. The results are leaner operations and improved levels of customer satisfaction.
Stronger Security
Biometric AIDC technologies ensure secure access to sensitive physical areas and environments, safeguarding both tangible and digital assets. By relying on unique physiological identifiers for authentication, biometric AIDC ensures that only authorized personnel are granted access to sensitive physical areas and online/offline resources.
Bottom Line: Automating ID and Data Collection
Despite being a relatively older set of technologies, automated identification and data collection (AIDC) continues to drive innovation and operational efficiency in modern enterprises and industries. Businesses apply the wide range of technologies to an even wider range of use cases that automate data collection, enhance accuracy, streamline operations, and improve security.
Because it’s cost effective to implement, accurate, generally easy to use, and useful in many different applications, AIDC has become an indispensable tool in today’s data-driven world and will likely hold its place for the indefinite future.
To learn more about software to help turn collected data into actionable insights, read Top 7 Data Analytics Tools next.